Periodontitis treatment
- Homepage
- Services
- Periodontology
- Periodontitis treatment
Services

Periodontitis treatment
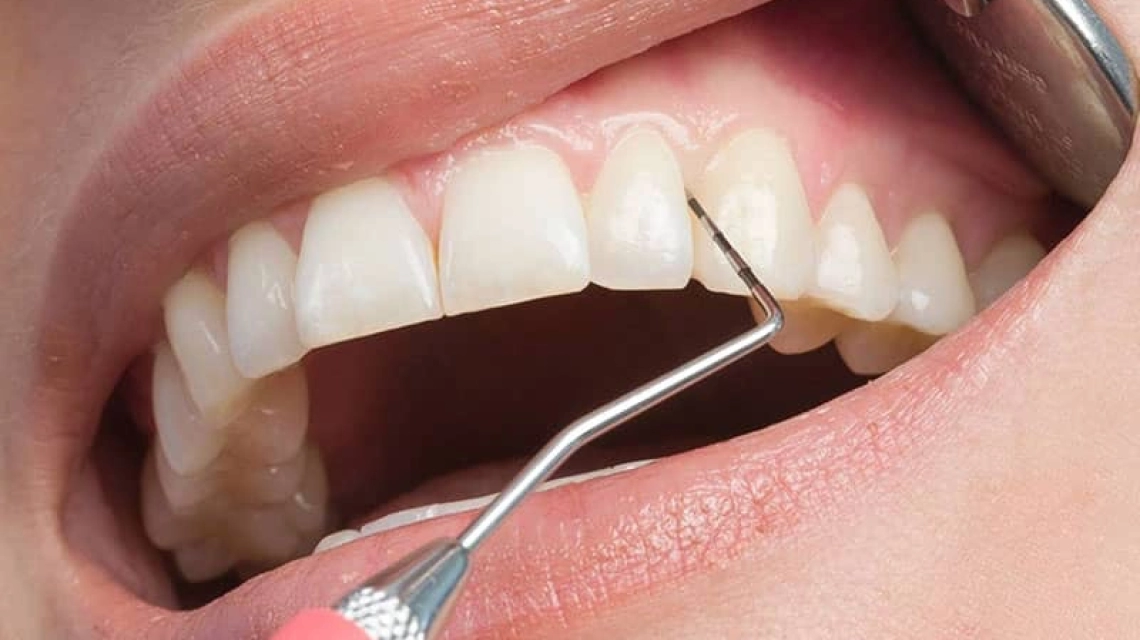
Periodontitis is a more advanced and severe form of gum disease compared to gingivitis. It is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the support structures around the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament and the facet bone. If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss and can have systemic effects on overall health.
Periodontitis usually develops from untreated gingivitis, where plaque and tartar build up on the teeth, causing inflammation and infection. As the disease progresses, pockets can form between the teeth and gums, creating spaces where more bacteria can accumulate.
Common signs and symptoms of periodontitis include:
- Receding gums
- Formation of pockets
- Bleeding gums
- Formation of gingival glands
- Tooth mobility
- Pain or discomfort
Periodontitis is categorized into different stages based on the severity of the disease:
- Mild periodontitis
- Moderate periodontitis
- Severe periodontitis
Treatment of periodontitis often involves a combination of professional dental interventions and improved oral hygiene practices by the individual. Some common treatments include:
- Scraping the roots
- Periodontal surgery
- Antibiotics
- Oral hygiene
- Smoking cessation
- Systematic dental check-ups
Regular follow-up visits with a dentist or periodontist are vital to monitor treatment progress and maintain oral health. Early diagnosis and intervention is key to preventing the progression of periodontitis and minimizing its impact on overall health.
- Clinic Address
Kimonos 6, Marousi 151 22 - Contact e-mail
info@dimopoulou-dental.gr - Contact Phone
+30 210 8029463 - Clinic hours
Mon - Wed 12:00 AM - 9:00 PM
Friday - 12:00 AM - 9:00 PM
Saturday Sunday - Closed
